Introduction to V Squats
Get Your Glutes in Gear: The Complete V Squat Tutorial
The V squat exercise is a highly effective lower body movement that targets the glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps. It is a variation of the traditional squat that places more emphasis on glute development. Developing strong and well-defined glutes is not only aesthetically pleasing but also crucial for overall fitness and health. The glute muscles play a significant role in stabilizing the pelvis, improving posture, preventing lower back pain, and enhancing athletic performance.
Key Takeaways
- V Squat is an effective exercise for glute development
- Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing results and avoiding injury
- Variations and resistance bands can increase difficulty and intensity
- Warming up and nutrition play important roles in glute development
- Progressively overloading the V Squat is key for continued results
Benefits of the V Squat for Glute Development
One of the primary benefits of incorporating the V squat into your workout routine is its ability to target multiple muscles in the lower body simultaneously. Unlike traditional squats that primarily focus on quadriceps development, V squats engage both the quads and glutes to a greater extent. This increased muscle activation leads to improved strength and power in these muscle groups.
In addition to strength gains, performing V squats can also enhance athletic performance by improving explosiveness and agility. The explosive nature of this exercise helps develop fast-twitch muscle fibers responsible for quick movements required in sports such as sprinting or jumping.
Furthermore, if your goal is to increase muscle size and definition in your glutes, incorporating V squats into your training regimen can be highly beneficial. By challenging these muscles with heavy loads or high repetitions over time, you can stimulate hypertrophy (muscle growth) resulting in rounder and firmer buttocks.
Proper Form and Technique for the V Squat
To maximize results while minimizing injury risk during V squats, it's essential to maintain proper form and technique throughout each repetition.
Firstly, foot placement plays a crucial role in targeting specific areas of your lower body during this exercise. Positioning your feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart with toes pointed outward at an angle will emphasize glute activation while still engaging other leg muscles effectively.
Secondly, achieving an appropriate depth in the squat is essential. Lowering your body until your thighs are parallel to the ground ensures optimal muscle activation and range of motion. However, it's important to avoid going too low as this can place excessive stress on the knees.
Maintaining proper spine and hip alignment is another key aspect of performing V squats correctly. Keep your chest lifted, shoulders back, and core engaged throughout the movement. Avoid rounding or arching your back as this can lead to lower back strain.
Lastly, paying attention to breathing techniques during V squats can help stabilize your core and enhance overall performance. Inhale deeply before descending into the squat position and exhale forcefully as you push through your heels to return to a standing position.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Performing the V Squat
| Common Mistakes | Impact | How to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Leaning too far forward | Places excessive strain on lower back and knees | Keep chest up and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement |
| Not engaging glutes and hamstrings | Reduces effectiveness of exercise and places more strain on quads | Focus on pushing through heels and squeezing glutes at the top of the movement |
| Allowing knees to cave in | Places excessive strain on knees and can lead to injury | Keep knees in line with toes throughout the movement |
| Using too much weight | Increases risk of injury and reduces effectiveness of exercise | Start with lighter weight and focus on proper form before increasing weight |
| Not using a full range of motion | Reduces effectiveness of exercise and limits mobility | Lower down until thighs are parallel to the ground and push up through heels to fully extend hips |
While performing V squats, it's crucial to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder progress or increase injury risk.
One common mistake is leaning too far forward during the movement. This places excessive stress on the lower back instead of targeting the glutes effectively. To avoid this error, focus on keeping an upright posture throughout each repetition by engaging your core muscles.
Another mistake is arching the back excessively at any point during the exercise. This not only compromises form but also increases strain on both spinal discs and surrounding muscles. Maintain a neutral spine position by tucking in your tailbone slightly while keeping a natural curve in your lower back.
Allowing knees to cave inward is another error that should be avoided when performing V squats or any squat variation for that matter. This puts unnecessary stress on knee joints and increases injury risk over time. Instead, focus on pushing knees outward in line with toes throughout each repetition while maintaining proper foot placement.
Lastly, not engaging glute muscles enough during V squats can limit their effectiveness for glute development specifically. Concentrate on squeezing your glutes forcefully at the top of each rep for maximum muscle activation. This mind-muscle connection will help you achieve better results and prevent other muscles from compensating for weak glutes.
How to Incorporate the V Squat into Your Workout Routine
To reap the full benefits of V squats, it's important to incorporate them strategically into your workout routine.
Frequency and volume recommendations for V squats depend on individual goals, fitness level, and recovery capacity. However, a general guideline is to perform this exercise 2-3 times per week with at least one day of rest in between sessions. Beginners may start with lower volume (e.g., 2 sets of 10-12 reps) and gradually increase as they become more comfortable and stronger.
Combining V squats with other exercises that target different muscle groups can create a well-rounded lower body workout routine. For example, pairing V squats with Romanian deadlifts or lunges can provide additional stimulus to hamstrings and quadriceps while still emphasizing glute development.
A sample workout plan could include starting with a dynamic warm-up followed by performing 3-4 sets of 8-10 reps of V squats using challenging weights or resistance bands. After completing the desired number of sets for V squats, move on to other exercises such as lunges or hip thrusts before finishing off with some glute-specific isolation exercises like donkey kicks or fire hydrants.
Variations of the V Squat for Increased Difficulty
Once you have mastered the basic form of the V squat, there are several variations you can incorporate into your routine to increase difficulty levels and continue making progress.
Adding weight is one way to intensify your workouts when performing V squats. You can use dumbbells held at shoulder height or a barbell placed across your upper back for added resistance. Gradually increasing weight over time will challenge your muscles further and promote continued strength gains.
Changing foot placement is another effective way to vary the stimulus during V squats. Experimenting with a wider or narrower stance can shift emphasis onto different muscle groups within the lower body. For example, a wider stance will target glutes and adductors more, while a narrower stance will engage quadriceps to a greater extent.
Using a stability ball or Bosu ball can also increase difficulty by challenging your balance and stability during V squats. Placing one foot on top of the ball while performing the exercise adds an element of instability that requires additional core activation and coordination.
How to Use Resistance Bands with the V Squat
Incorporating resistance bands into your V squat routine can provide unique benefits and further enhance glute development.
Using resistance bands adds accommodating resistance throughout the entire range of motion, making it more challenging at peak contraction when compared to using free weights alone. This increased tension stimulates muscle fibers effectively, leading to greater strength gains and muscle growth over time.
To use resistance bands with V squats, you can either attach them around your thighs just above your knees or loop them under both feet while holding their handles at shoulder height. The band placement depends on personal preference and desired level of difficulty.
A sample workout plan using resistance bands could involve performing 3-4 sets of 12-15 reps of banded V squats after completing regular weighted sets for maximum glute activation. Alternatively, you could perform supersets alternating between banded V squats and other exercises such as lateral band walks or clamshells for added variety and challenge.
The Importance of Warming Up Before Performing the V Squat
Warming up before any exercise is crucial for injury prevention, improved performance, and optimal muscle activation during workouts.
Benefits of warming up include increased blood flow to muscles, enhanced joint mobility, improved neuromuscular coordination, elevated core temperature, reduced risk of strains or sprains, and improved mental focus.
Before performing V squats, it's recommended to start with a general warm-up that includes light cardiovascular exercise such as jogging or cycling for 5-10 minutes. This increases blood flow and raises your body temperature, preparing your muscles for more intense activity.
After the general warm-up, it's important to perform specific warm-up exercises that target the muscles involved in V squats. Dynamic stretches and mobility drills can help increase range of motion and activate key muscle groups. Examples of specific warm-up exercises for V squats include bodyweight squats, walking lunges, hip circles, or glute bridges.
Tips for Maximizing Glute Activation During the V Squat
To maximize glute activation during V squats and ensure you are effectively targeting these muscles, consider implementing the following tips:
Firstly, establish a strong mind-muscle connection by consciously focusing on engaging your glutes throughout each repetition. Visualize squeezing your glutes forcefully at the top of each squat to enhance muscle activation.
Secondly, pause briefly at the bottom of each rep before ascending back up. This momentary pause allows you to fully engage your glutes before initiating upward movement again.
Lastly, using a slower tempo during both eccentric (lowering) and concentric (lifting) phases of the squat can increase time under tension on your glutes. Slowing down the movement also helps maintain control and proper form throughout each repetition.
How to Progressively Overload the V Squat for Continued Results
Progressive overload is essential for continued results when performing any exercise including V squats. It involves gradually increasing demands placed on muscles over time to stimulate further adaptation and growth.
One way to progressively overload during V squats is by increasing weight or resistance used in each workout session as you become stronger. Gradually adding more weight challenges your muscles further and promotes ongoing strength gains.
Another method is changing tempo or volume of your V squat workouts. Slowing down the eccentric phase (lowering) of the squat or increasing time under tension by performing more reps per set can provide a different stimulus to your muscles and promote further development.
It's important to note that progressive overload should be implemented gradually and within your individual capabilities. Pushing too hard or progressing too quickly can lead to overtraining, injury, or burnout. Listen to your body and make adjustments accordingly.
The Role of Nutrition in Glute Development
While exercise is crucial for glute development, proper nutrition plays an equally important role in achieving optimal results.
To support muscle growth and recovery, it's essential to consume adequate protein as part of a well-balanced diet. Protein provides the building blocks necessary for muscle repair and growth. Aim for a daily intake of 0.8-1 gram of protein per pound of body weight from sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based proteins.
In addition to protein intake, consuming enough calories is also important for muscle growth. To build glute muscles effectively while minimizing fat gain or loss during this process requires being in a slight caloric surplus (consuming more calories than you burn). However, it's crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods rather than relying solely on high-calorie processed foods.
Carbohydrates are another macronutrient that plays a vital role in providing energy for intense workouts required for glute development. Opt for complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables instead of simple sugars found in processed snacks or sugary drinks.
Lastly but not leastly healthy fats should also be included in your diet as they provide essential fatty acids necessary for hormone production and overall health. Sources include avocados,nuts seeds,fish,and olive oil among others
Frequently Asked Questions About the V Squat
1) How often should I perform the V squat?
The frequency of V squat workouts depends on individual goals, recovery capacity, and overall training program. As a general guideline, 2-3 times per week with at least one day of rest in between sessions is recommended. However, it's important to listen to your body and adjust accordingly.
2) Can I do the V squat with bad knees?
If you have knee issues or pain, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before attempting any exercise that involves knee flexion such as squats. They can assess your condition and provide appropriate modifications or alternative exercises that are safe for your knees.
3) Is the V squat better than traditional squats for glute development?
Both V squats and traditional squats can effectively target glutes when performed correctly. The choice between them depends on personal preference, individual biomechanics, and specific goals. Some individuals may find one variation more comfortable or effective than the other.
Tips for Avoiding Injury While Performing the V Squat
To minimize injury risk while performing V squats:
1) Prioritize proper form and technique over weight lifted.
2) Gradually increase weight or resistance used.
3) Listen to your body - if something feels off or painful during an exercise session, stop immediately.
4) Incorporate adequate rest days into your training routine.
5) Consider working with a qualified fitness professional who can guide you through proper form and technique.
Incorporating the V squat into your workout routine can be highly beneficial for glute development as well as overall lower body strength and power. By targeting multiple muscles simultaneously in the lower body region, this exercise promotes muscle growth, enhances athletic performance,and improves overall fitness levels.
Remember to prioritize proper form and technique when performing V squats to maximize results while minimizing injury risk. Avoid common mistakes such as leaning too far forward or allowing knees to cave in. Instead, focus on engaging your glutes throughout each repetition and maintaining proper alignment.
To continue making progress, consider incorporating variations of the V squat into your routine, using resistance bands for added challenge, and progressively overloading your workouts over time. Additionally, pay attention to nutrition by consuming adequate protein and calories to support muscle growth.
By following these guidelines and incorporating V squats into your workout routine consistently, you can achieve optimal glute development and enjoy the benefits of stronger lower body muscles for overall fitness and health.
FAQs
What is the V squat?
The V squat is a variation of the traditional squat exercise that targets the glutes, quads, and hamstrings. It involves standing on a V-shaped platform and performing a squatting motion.
What are the benefits of V squats?
V squats can help to strengthen and tone the glutes, quads, and hamstrings. They can also improve overall lower body strength, stability, and balance. Additionally, V squats can be a good alternative for those who experience discomfort or pain when performing traditional squats.
How do I perform a V squat?
To perform a V squat, stand on the V-shaped platform with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes pointing slightly outward. Hold onto the handles for balance and lower your body down into a squatting position, keeping your back straight and your knees in line with your toes. Push through your heels to stand back up and repeat for desired reps.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when performing V squats?
Common mistakes when performing V squats include leaning too far forward, allowing your knees to cave inward, and not lowering your body down far enough. It's important to maintain proper form throughout the exercise to avoid injury and maximize results.
Can V squats be modified for beginners?
Yes, V squats can be modified for beginners by using a lighter weight or no weight at all, and by performing the exercise with a shallower range of motion. It's important to start with a comfortable weight and gradually increase as strength and technique improve.
V Squats, also known as the V Squat machine, are a popular exercise option in many gyms. This unique piece of equipment offers a different variation of the traditional squat movement, targeting the lower body muscles in a slightly different way. V Squats provide an excellent opportunity to work on quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes while reducing stress on the lower back compared to traditional free weight squats.
The V Squat machine consists of a sled with two angled platforms, forming a V shape. The user stands on the platforms and grasps the handles for stability while performing the exercise. The resistance is typically provided by adding weight plates to the sled.
The V Squat machine allows for a more upright torso position throughout the movement, putting less strain on the lower back. This is especially beneficial for individuals with lower back issues or those who struggle to maintain proper form during traditional squats.
By incorporating V Squats into your lower body training routine, you can effectively target your quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes while minimizing the risk of injury. Whether you are a beginner looking to strengthen your leg muscles or an experienced lifter aiming to switch up your routine, V Squats can be a valuable addition to your workout regimen.
Benefits of V Squats
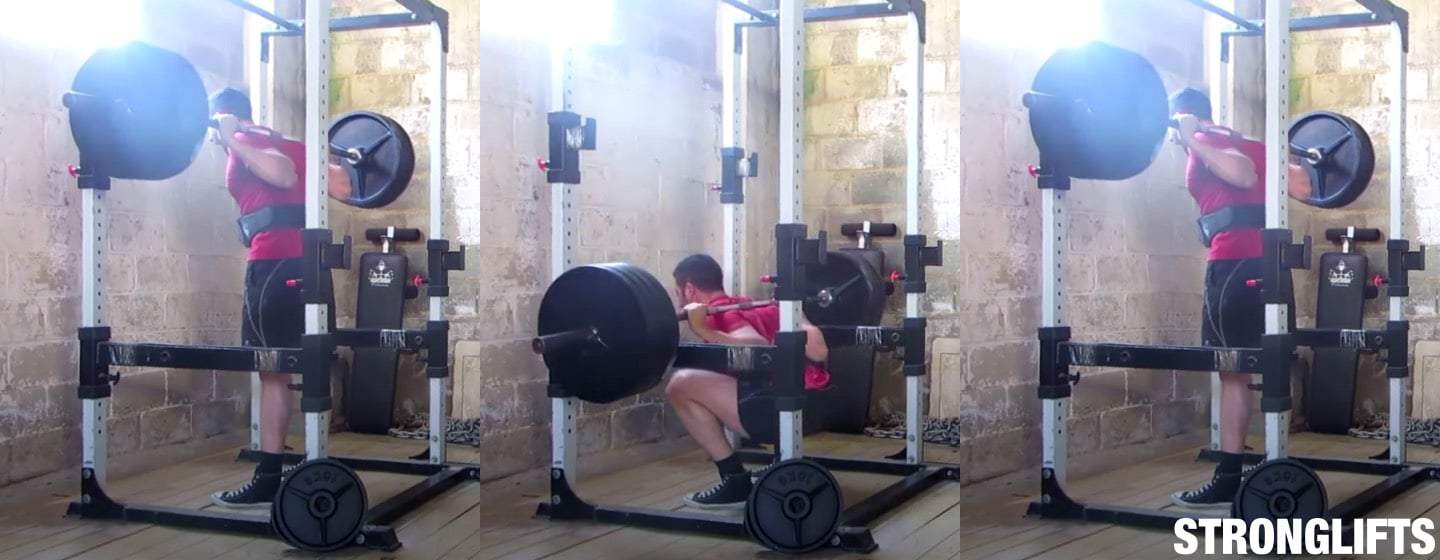

V Squats offer several notable benefits for individuals looking to strengthen their lower body muscles. Here are some of the key advantages of incorporating V Squats into your workout routine:
- Increased Quadriceps Activation: V Squats target the quadriceps muscles in the front of the thighs more effectively than traditional squats. The unique V-shaped platform allows for a greater range of motion, leading to increased muscle activation and development in the quads.
- Enhanced Hamstring Engagement: V Squats also engage the hamstrings, which are crucial for lower body strength and stability. The movement pattern of the exercise places additional emphasis on the hamstrings, leading to improved muscle development and overall lower body balance.
- Glute Strengthening: The V Squat machine allows for deeper squatting and greater glute activation compared to regular squats. This helps to effectively target and strengthen the gluteal muscles, promoting better hip stability and overall lower body power.
- Reduced Lower Back Strain: The V Squat machine helps individuals maintain a more upright torso position throughout the movement, reducing stress on the lower back. This makes it an excellent option for individuals with lower back issues or those who struggle to maintain proper form during traditional squats.
- Safety and Stability: The V Squat machine provides added stability and support, making it a safe exercise option for individuals who may have difficulty balancing during free weight squats. The sled and handles allow for better control and minimize the risk of injury.
Incorporating V Squats into your workout routine can help you target specific muscle groups, improve overall lower body strength, and minimize the risk of injury. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced lifter, V Squats can be a valuable addition to your lower body training regimen.
Proper Form and Technique for V Squats
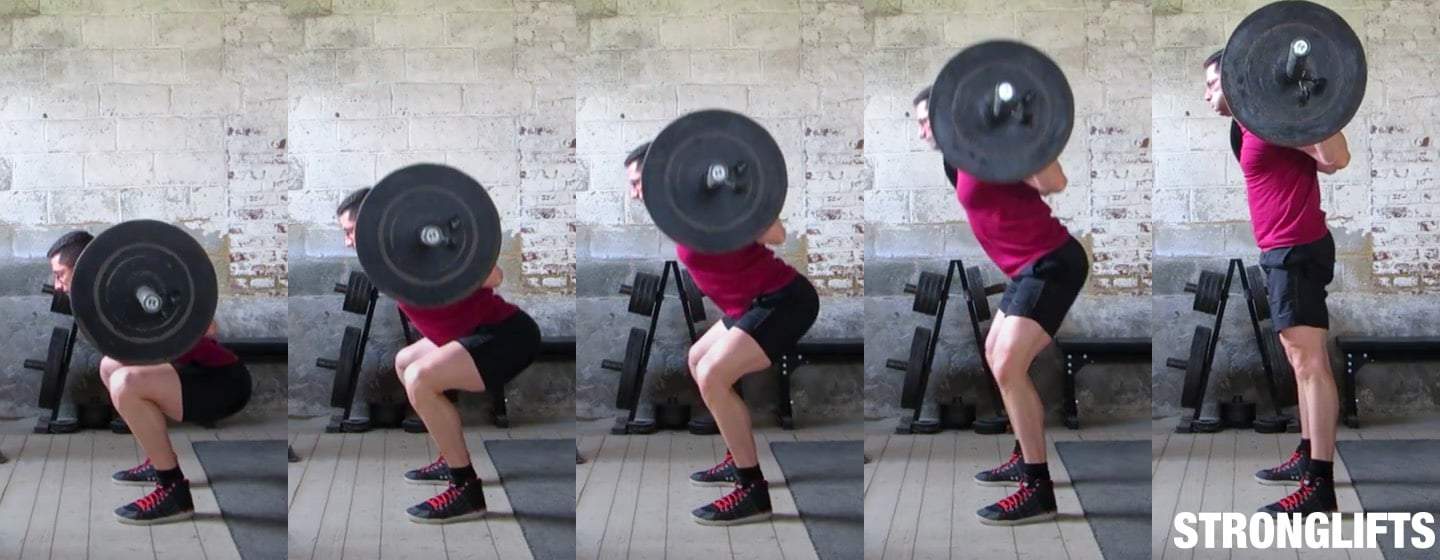

When performing V Squats, it is important to maintain proper form and technique to maximize the effectiveness of the exercise and minimize the risk of injury. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart on the V-shaped platform of the machine. The heels should be slightly elevated, and toes should be pointing slightly outward.
- Position yourself so that the pads or shoulder rests of the machine are resting comfortably on your shoulders, just above your traps.
- Engage your core and maintain a tall posture throughout the entire movement. Keep your chest up and your shoulders back.
- As you descend into the squat, initiate the movement by pushing your hips back, bending your knees, and lowering your body down. Keep your knees in line with your toes.
- Aim to reach a 90-degree angle at the knees, or lower if you have the flexibility. Make sure to maintain control and avoid bouncing at the bottom of the movement.
- Push through your heels and drive your body back up to the starting position, fully extending your hips and knees.
- Throughout the entire movement, focus on keeping your knees stable and tracking in line with your toes. Avoid letting your knees cave inward.
Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as you become more comfortable and confident in your form. It may also be beneficial to seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure proper execution of V Squats.
Key Muscles Targeted in V Squats
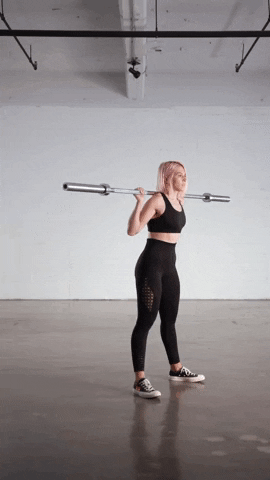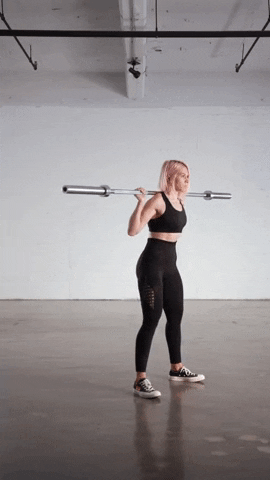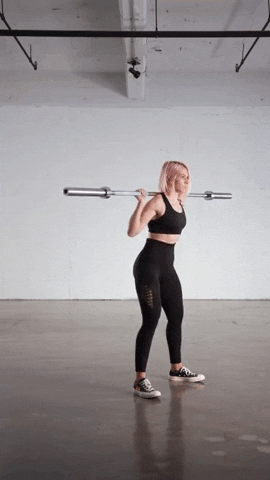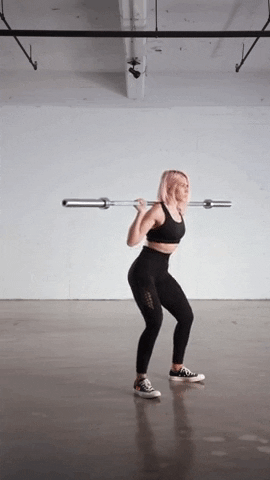
V squats are a highly effective compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the lower body. Here are the key muscles targeted in V squats:
- Quadriceps: The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, are the primary muscle group engaged in V squats. As you descend into the squat, the quadriceps contract to extend the knees and power the upward movement.
- Hamstrings: The hamstrings, located at the back of the thigh, act as stabilizers during V squats. They assist in bending the knees and help maintain balance and control throughout the exercise.
- Glutes: The gluteal muscles, including the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, are also heavily engaged in V squats. These muscles work to extend the hips and maintain stability throughout the movement.
- Calves: The calf muscles, specifically the gastrocnemius and soleus, play a secondary role in V squats. They help to stabilize the lower leg and assist in pushing through the heels during the upward phase of the squat.
- Core: While V squats primarily target the lower body, they also engage the core muscles to maintain stability and proper posture. This includes the rectus abdominis, obliques, and erector spinae.
By targeting these key muscles, V squats provide a comprehensive lower body workout that can help improve lower body strength, power, and overall muscular development when performed with proper form and technique.
Quadriceps and Hamstrings Activation
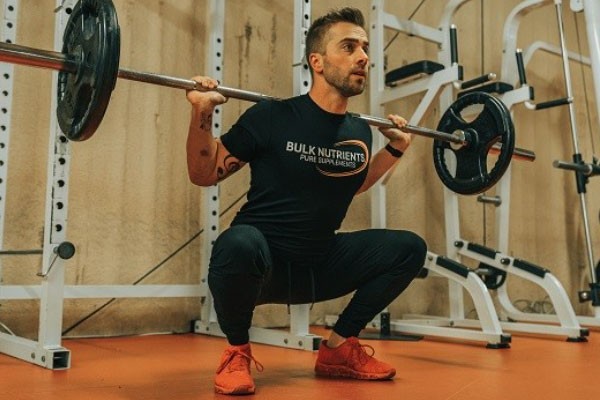

During V squats, the quadriceps and hamstrings are key muscle groups that are activated. The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, are responsible for knee extension and play a primary role in V squats. As you descend into the squat position, the quadriceps contract to extend the knees, generating power for the upward movement.
In addition to the quadriceps, the hamstrings, located at the back of the thigh, also play a crucial role in V squats. While they act as stabilizers during the exercise, they assist in bending the knees and help maintain balance and control throughout the movement.
When performing V squats correctly, the quadriceps and hamstrings work together in a coordinated effort to provide strength and stability to the lower body. This dual muscle activation helps to improve overall lower body strength and power.
To maximize activation of these muscle groups during V squats, it is important to maintain proper form and technique. This includes keeping the knees aligned with the toes, ensuring a full range of motion, and distributing the weight evenly through the feet.
By engaging the quadriceps and hamstrings in V squats, individuals can develop stronger and more defined thighs, enhance athletic performance, and improve functional movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
Glute Engagement in V Squats
During V squats, the glutes, or the muscles of the buttocks, are also highly engaged. This muscle group plays a vital role in stabilizing the hips and lower back during the exercise.
To maximize glute activation in V squats, it is important to focus on proper form and technique. By consciously squeezing the glutes at the top of the movement, individuals can ensure that these muscles are fully engaged throughout the exercise.
The glutes are activated primarily during the upward phase of the squat. As you push through the heels to rise back up to the starting position, the glutes contract to extend the hips. This movement not only adds power to the movement but also helps to shape and strengthen the gluteal muscles.
Engaging the glutes in V squats offers numerous benefits including improved lower body strength, enhanced athletic performance, and greater aesthetic appeal. Strong glutes can also help support proper posture, reduce the risk of lower back pain, and improve functional movements such as running, jumping, and climbing stairs.
Incorporating glute activation exercises, such as hip thrusts and glute bridges, into your training routine can further strengthen and develop these muscles. Combining these exercises with V squats can result in well-rounded glute development and overall lower body strength.
By ensuring proper glute engagement in V squats, individuals can maximize their workout and achieve optimal results.
Equipment and Set-Up for V Squats
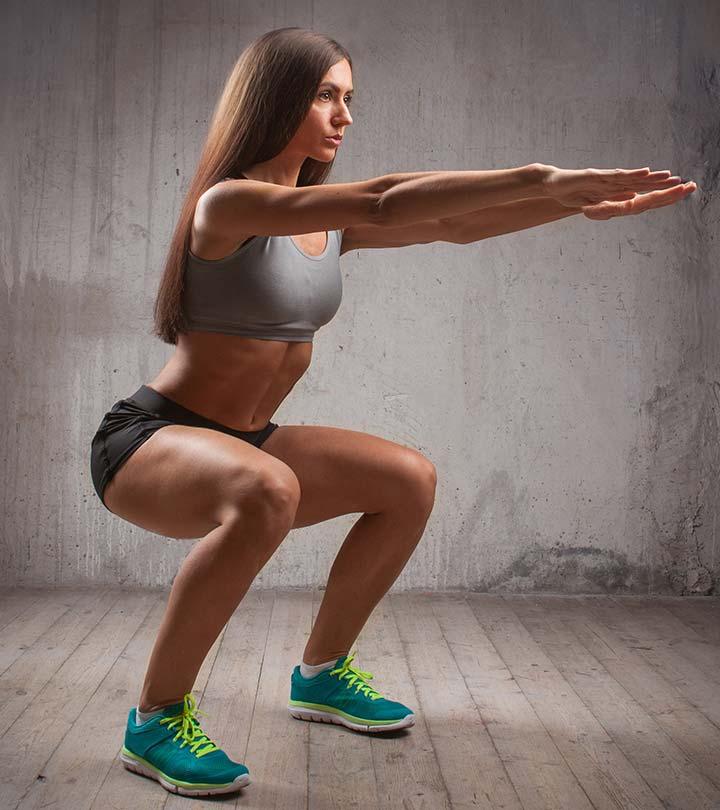

To perform V squats effectively, it is important to have the right equipment and set it up properly. One of the most common equipment used for V squats is a V squat machine. This machine is specifically designed to target the muscles in the lower body and provide stability during the exercise.
When choosing a V squat machine, it is essential to ensure that it is of good quality and can withstand the weight you will be using. Look for a machine that has a sturdy frame, adjustable seat and footplates, and a secure safety mechanism.
Before starting your V squat exercise, it is important to adjust the machine to your specific needs. Begin by setting the height of the seat so that your thighs are parallel to the ground when you are in the bottom position of the squat. Adjust the footplates so that they are at a comfortable distance apart and are evenly aligned with your feet.
Once the machine is set up, make sure to position yourself correctly on it. Place your feet on the footplates, ensuring that they are shoulder-width apart and are parallel to each other. Align your knees with your toes and position your back flat against the seat.
By taking the time to properly set up the equipment for V squats, you can ensure maximum safety and effectiveness during your workout.
Choosing the Right V Squat Machine

Adjusting the V Squat Machine for Proper Form

When using a V squat machine, it is crucial to adjust it properly to ensure you maintain proper form throughout the exercise. Here are some steps to follow for adjusting the V squat machine for proper form:
- Seat Position: Start by adjusting the seat height so that when you sit on the machine, your knees are at a 90-degree angle when your feet are on the foot platform. This alignment will help you maintain proper form and prevent excessive strain on your knees.
- Foot Platform Placement: Next, adjust the foot platform so that your feet are shoulder-width apart. This position will provide stability and allow for proper activation of the targeted muscles.
- Back Support: Depending on the machine, there may be a back support or pad available. Adjust it so that it provides support to your lower back without causing any discomfort. This will help you maintain a neutral spine throughout the exercise.
- Knee Alignment: Ensure that the knee pads or leg supports are positioned correctly to align with your knees. This alignment will help prevent any inward or outward movement of the knees, promoting proper tracking and reducing the risk of injury.
By following these steps and adjusting the V squat machine accordingly, you can ensure that you maintain proper form and maximize the effectiveness of your V squat workout. Remember to always start with lighter weights or resistance and gradually increase as your strength and technique improve.
Proper Execution of V Squats
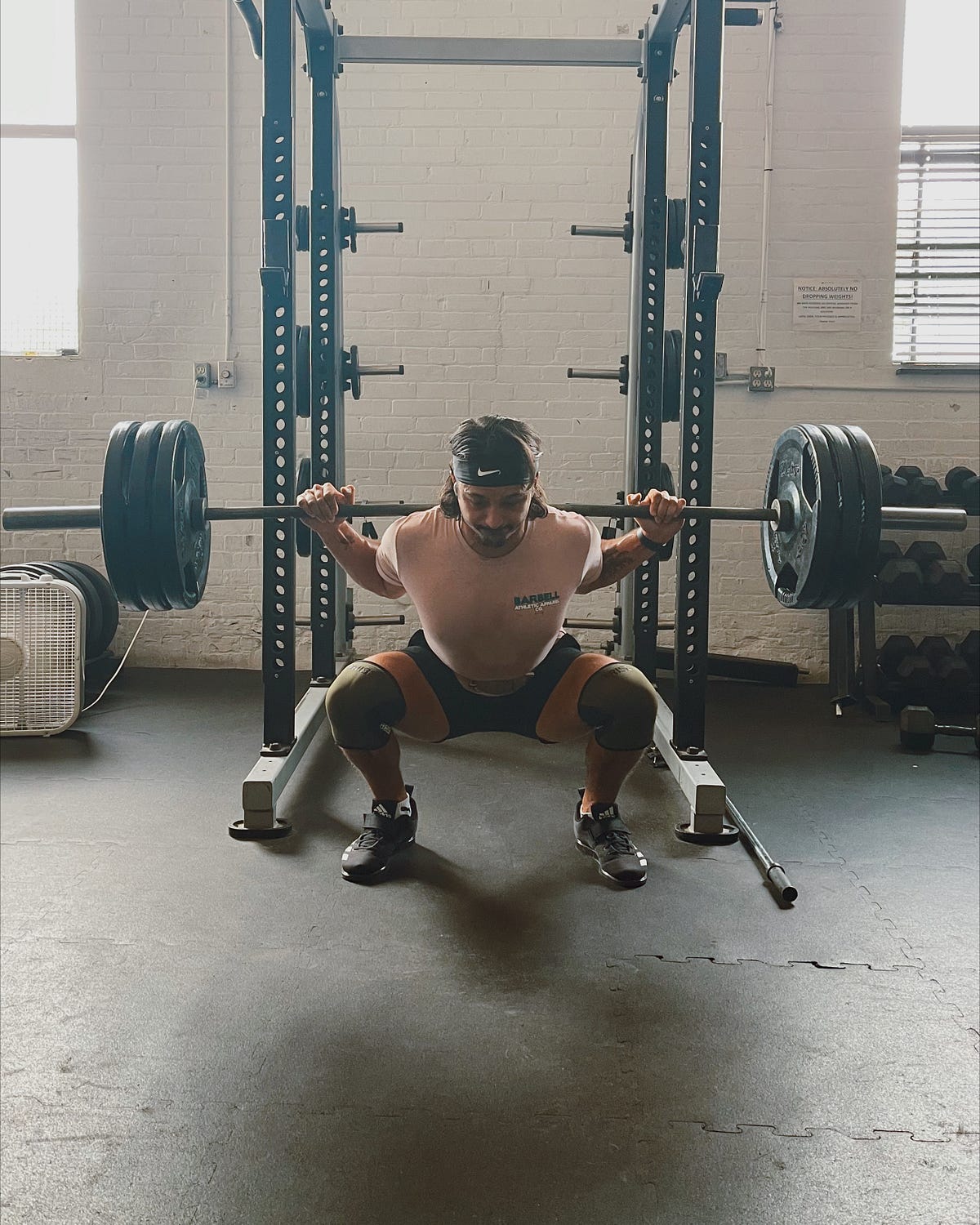

To perform V squats with proper execution and maximize their effectiveness, it is important to follow the correct technique. Here are the steps to execute V squats properly:
- Starting Position and Feet Placement: Begin by standing on the foot platform with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes slightly pointing outward. Hold onto the handles or bars for stability if necessary.
- Movement and Depth: Initiate the squat by bending at the knees and hips simultaneously, maintaining a neutral spine throughout the movement. Lower your body until your thighs are parallel to the ground or slightly below. Keep your chest upright and your core engaged.
- Controlled Descent and Ascent: Lower yourself into the squat position in a controlled manner without bouncing or jerking. Once you reach the desired depth, push through your heels and drive your body back up to the starting position, fully extending your hips and knees. Exhale during the ascent phase of the squat.
- Repeat the Movement: Complete the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Remember to start with lighter weights or resistance and gradually increase as you become more comfortable with the movement. This will help you build strength and avoid any potential injuries. Proper execution of V squats will target your quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes effectively, helping you achieve your fitness goals.
Starting Position and Feet Placement

Movement and Depth in V Squats
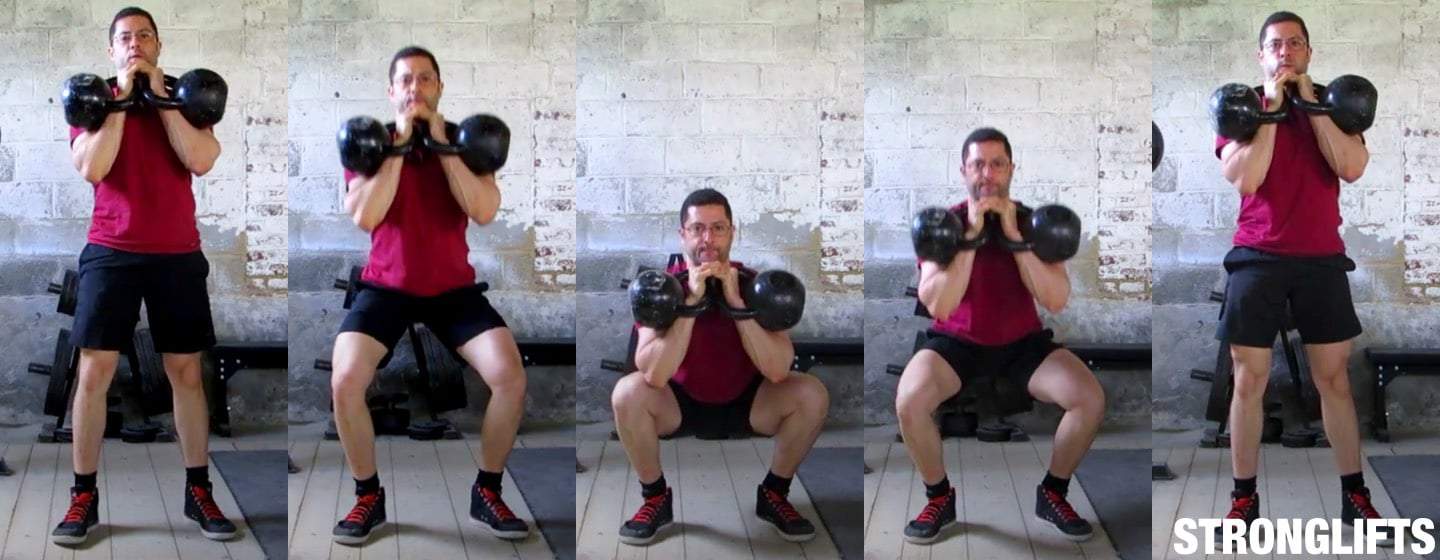

To perform V squats with proper form and technique, it is important to understand the movement and depth involved. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Starting Position:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes pointed slightly outward.
- Position yourself under the V squat machine, ensuring the padded shoulder rests are comfortably resting on your shoulders.
- Lowering Phase:
- Initiate the movement by bending at your hips and knees simultaneously.
- Lower your body down by pushing your hips back and keeping your chest lifted.
- Aim to lower your body until your thighs are parallel to the ground. This is considered a full squat depth.
- Ascending Phase:
- Push through your heels to straighten your legs and return to the starting position.
- Keep your core engaged and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
Tips and Recommendations:
- Focus on maintaining a controlled and steady movement throughout the exercise.
- Avoid bouncing or using momentum to complete the squat.
- Keep your knees in line with your toes and ensure they don't cave inward.
- Aim to maintain an upright posture and avoid excessive leaning forward.
- If you have any knee or joint issues, it is advisable to consult with a fitness professional before attempting V squats.
Remember, proper form and technique are crucial to reap the benefits of V squats while minimizing the risk of injury.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in V Squats

Avoiding Excessive Forward Lean
Avoiding Excessive Forward Lean:
One common mistake that people make while performing V squats is excessive forward lean. This occurs when the upper body leans too far forward during the squatting motion, placing excessive strain on the lower back and reducing the effectiveness of the exercise. To avoid this mistake and maintain proper form, it is essential to focus on a few key points.
Firstly, it is crucial to engage the core muscles and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement. This will help to stabilize the torso and prevent excessive forward lean. Engaging the core also helps to protect the lower back from injury.
Secondly, it is important to control the depth of the squat. Going too deep can cause the hips to shift forward, leading to an increased forward lean. It is recommended to squat until the thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly below, maintaining proper alignment of the torso and legs.
Additionally, paying attention to foot placement can also help prevent excessive forward lean. Positioning the feet shoulder-width apart and pointing them slightly outward can improve stability and balance during the squat.
Lastly, focusing on maintaining an upright chest position throughout the movement can also help prevent excessive forward lean. This can be achieved by imagining a string pulling the chest upwards, keeping the shoulders back and down.
By following these guidelines and concentrating on maintaining proper form, individuals can avoid the mistake of excessive forward lean and maximize the benefits of V squats.
Preventing Knee Cave in V Squats
Preventing Knee Cave in V Squats:
One common mistake that individuals make while performing V squats is allowing their knees to cave inwards during the movement. This can put undue stress on the knees and compromise proper form, potentially leading to injury. To prevent knee cave and maintain proper alignment in V squats, it is important to focus on a few key points.
Firstly, individuals should pay attention to their feet placement. Positioning the feet shoulder-width apart and slightly pointing the toes outward can help promote proper alignment of the knees. This will ensure that the knees track in line with the toes throughout the squatting motion.
Secondly, engaging the glute muscles is crucial in preventing knee cave. By actively squeezing the glutes during the movement, individuals can help stabilize the hips and prevent them from shifting inward.
Additionally, individuals should be mindful of their hip and pelvic positioning. Keeping the pelvis in a neutral position and maintaining a slight arch in the lower back can also help prevent knee cave. It is important to avoid excessive rounding or tucking of the pelvis, which can contribute to improper knee alignment.
Lastly, individuals can use visual cues or props to help prevent knee cave. For example, using a resistance band around the thighs can provide feedback and resistance against knee cave. The individual can actively push against the band, promoting proper knee alignment.
By following these guidelines and focusing on proper alignment, individuals can prevent knee cave in V squats and ensure the safety and effectiveness of the exercise.
Variations and Progressions in V Squats
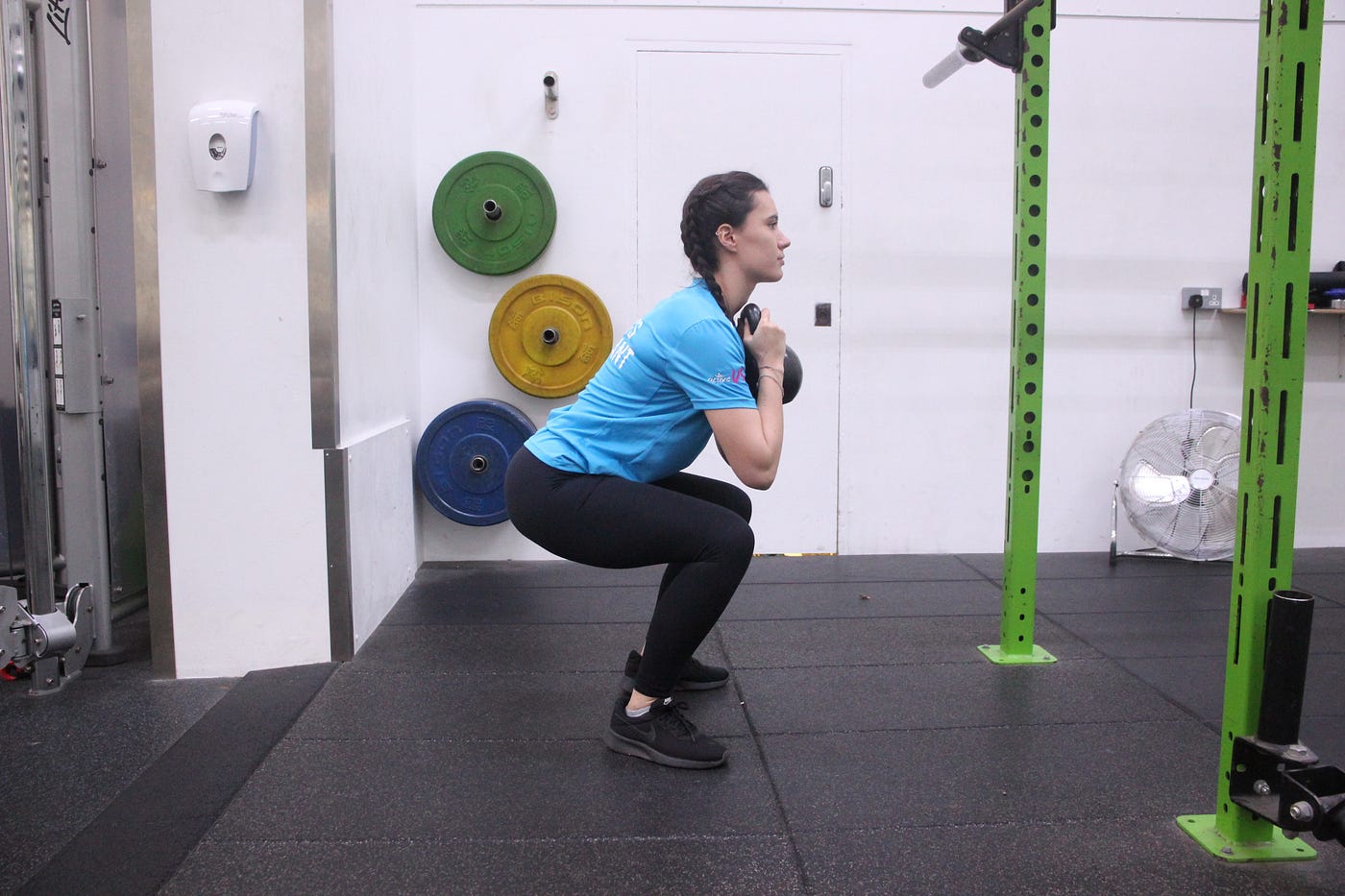

Adding Weight and Resistance in V Squats
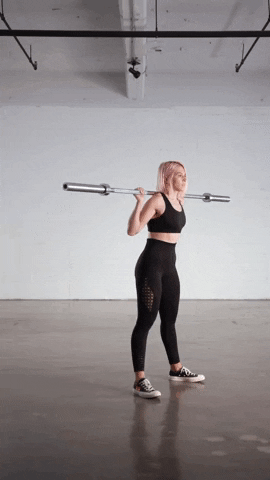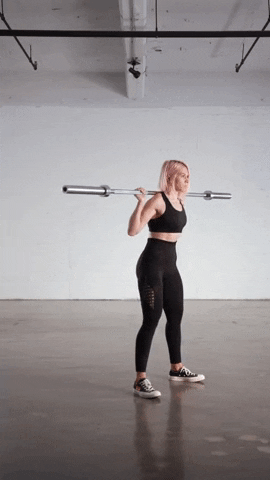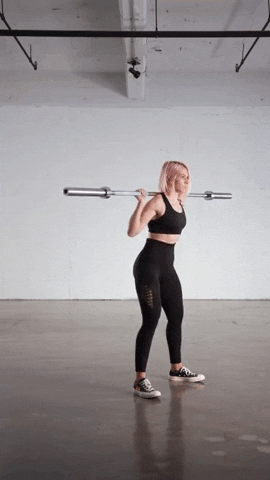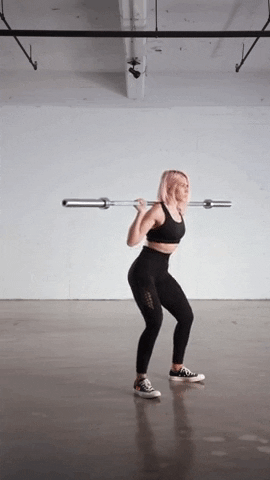
Adding weight and resistance to your V Squats can help increase the intensity of the exercise and further challenge your muscles. Here are a few ways you can add weight and resistance to your V Squat workouts:
- Barbell Squats: One common method of adding weight to your V Squats is by incorporating a barbell. With this method, you can either use the V Squat machine with a barbell loaded on your back, or you can perform traditional barbell squats in a V position. This allows you to increase the load on your muscles and build strength.
- Dumbbell or Kettlebell Goblet Squats: Another option is to hold a dumbbell or kettlebell in front of your chest during the V Squat. This added weight will increase the resistance on your legs, making the exercise more challenging and beneficial.
- Resistance Bands: Adding resistance bands can also be an effective way to increase the difficulty of your V Squat. You can attach the bands to the V Squat machine or anchor them to a stationary object, and then loop them around your shoulders or thighs. The bands provide continuous tension throughout the movement, activating your muscles even more.
- Weighted Vest or Belt: If you prefer a more versatile option, you can wear a weighted vest or a weight belt during your V Squat workouts. These accessories allow you to add weight to your body without the need for additional equipment, making them convenient and adaptable.
By incorporating these weight and resistance methods into your V Squat routine, you can continue to challenge your muscles, promote muscle growth, and improve your overall strength and fitness level. Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as your strength progresses.
Single-Leg V Squats and Other Variations
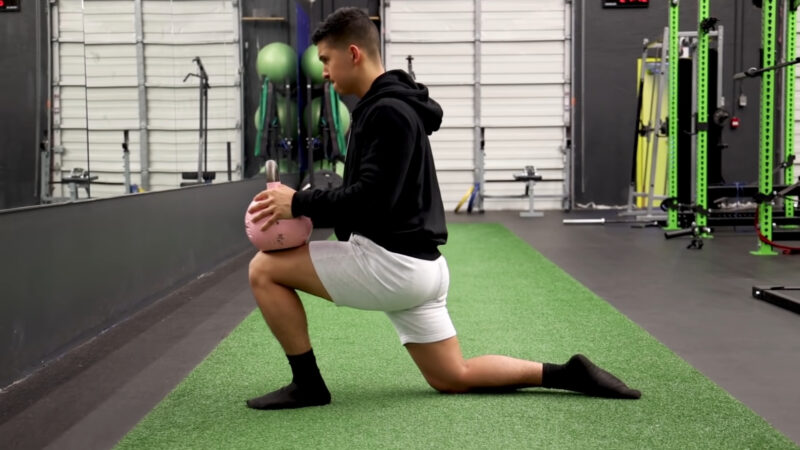

Single-leg V squats, also known as Bulgarian split squats, are an advanced variation of the V squat that further challenges your balance, stability, and leg strength. To perform a single-leg V squat, begin by placing one foot on a raised surface behind you, such as a weight bench or step. The other leg should be positioned in front of you, forming a V shape with your feet.
Lower your body down into a squat position, keeping your weight on the front leg and maintaining a straight back. Push through your front heel to stand back up, focusing on engaging your quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes throughout the movement. Switch legs and repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
In addition to single-leg V squats, there are other variations of the V squat that can be incorporated into your workout routine to add variety and challenge. Some examples include:
- Wide Stance V Squats: Instead of placing your feet in a narrow V position, widen your stance to target your inner thighs and add extra emphasis on your glutes.
- Jumping V Squats: Add plyometric power to your V squat by incorporating a jump at the top of the movement. This explosive variation helps improve leg power and cardiovascular endurance.
- Pause Rep V Squats: Introduce isometric holds into your V squat by pausing at the bottom of the movement for a few seconds before driving back up. This variation increases time under tension and can enhance muscle growth and strength.
By incorporating these variations into your V squat routine, you can continuously challenge your muscles, prevent boredom, and ensure well-rounded lower body development. Remember to start with proper form and gradually increase the difficulty as you progress.
